When most marketers think of SEO, they imagine clever keyword research, high-quality content creation, and sleek tactics for acquiring backlinks.
Yet, these are all on-page and off-page SEO techniques, as technical SEO factors often get overlooked.
While fixing broken links and improving your loading times aren’t as exciting as content creation, technical SEO is still undeniably crucial if you want your content to rank.
For example, even if you have the highest quality content in the world, If Google isn’t able to crawl & index your site due to a technical issue, you won’t appear in the SERPs at all.
If on-page SEO is the brash movie star soaking up the glory and fame, technical SEO is the director working hard behind the scenes to make the movie a reality.
While the movie star’s charisma and daring stunts are what draws in the audience (stellar content), nobody would be able to bear witness to it without the director’s cameras (your technical SEO strategy).
Technical SEO involves tweaking your webpages so that they’re effortless for search engines to crawl & index them.
That means implementing a mobile-friendly site design, an organized site structure, optimized page speed, and a consistent URL structure – just to name a few technical aspects that affect SEO.
Even in the age of AI-powered content creation, technical SEO still matters, so stay tuned to learn how to master it.
Understanding Technical SEO
Most digital marketers will break down SEO into three core components; on-page SEO, off-page SEO, and technical SEO.

On-page SEO refers to everything you do to increase SERP (search engine results pages) rankings on your website. It primarily has to do with content that tells search engines what your website is about, such as meta descriptions, image alt text, headings, internal links, and keyword usage.
Off-page SEO is your SEO efforts that occur off your website, such as high-authority backlinks, guest blog posts, videos on platforms like YouTube, and social media marketing.
Technical SEO refers to your efforts to adhere to the technical requirements of search engines like Google & Bing. In addition to making it easier for search engines to crawl, index, and render your website, some technical SEO factors also improve user experience, like boosting your website’s loading times.
Search engine crawlers can become confused if your technical SEO isn’t on point, which can lead to you disappearing from the SERPs altogether.
Common factors that affect technical SEO include the following:
- Duplicate content issues
- Broken links
- XML sitemaps (or a lack of one)
- Structured data
- CSS & Javascript
- Schema markup
- Site architecture
- Indexing issues
- Poor load speed
- Mobile-friendliness
- 404 pages
- 301 redirects
- Hreflang attributes
As you can see, quite a bit goes into technical SEO, so you need a strong understanding of the fundamentals if you want your web pages to show up in the SERPS.
If you’ve got rock-solid content that’s optimized for relevant keywords, but you still aren’t seeing the results you want, technical issues may be the culprit.
It can be incredibly frustrating to lose organic traffic due to avoidable issues like broken links & 404 pages, so you need to take technical SEO seriously.
Why Does Technical SEO Still Matter in the Age of AI?
Now that intuitive AI platforms are widely used to generate content, is there still a need for technical SEO?
The answer is a definite yes.
While AI chatbots and content generators are indeed impressive, they still can’t account for technical aspects taking place behind the scenes.
Accordingly, you still need to keep a close eye on your technical SEO, ensuring that you don’t run into duplicate pages or indexing issues. Beyond that, you still need to implement an organized site structure if you want your content to get properly crawled & indexed.
If you upload your AI-generated content on orphan pages (web pages containing no internal links pointing to them), you can kiss all the potential organic traffic it could generate goodbye.
However, that’s not to say that there aren’t AI tools out there that can make technical SEO easier for you.
You can use AI tools to do the following:
- Automate the creation of XML sitemaps
- Generate JSON-LD schema
- Automate crawl directives
- Aid with programmatic content
Leveraging AI in this manner will help you automate certain aspects of your technical SEO strategy, which will free up a lot of your time to focus on other things.
Yet, it’s important to distinguish the difference between AI content generation and using AI to help with technical SEO. Generating AI content and mindlessly uploading it to your website won’t work, as you need to be more calculated than that.
If you can successfully blend AI content with rigorous technical SEO, you’ll see the best results.
A Crash Course in Technical SEO
Are you a total beginner to the technical aspects of search engine optimization?
Not to worry, as this brief yet informative crash course will teach you everything you need to know about the technical side of an SEO strategy.
That way, you’ll be able to start optimizing your website so that it’s easier for search engines to crawl, index, and render your website, which will help boost your online visibility immensely.
Using a flat site architecture
It’s imperative to start your technical SEO with your site architecture, as it will inform & guide the rest of your strategy. Lots of technical issues pop up because the site architecture isn’t optimal, so perfecting it from the get-go will help you avoid problems later on.
It’s akin to beginning on-page SEO work with in-depth keyword research.
In particular, you need to have a logical, organized site structure wherein every page is connected via internal links. Not only that, but each webpage should only be a few clicks away from the homepage.
That’ll make it extremely easy for search engine bots to crawl & index every page on your website.
If your site architecture is all over the place, you may inadvertently create orphan pages with no internal links.
That’s disastrous for your SEO, as it’ll be near impossible for bots to locate, crawl, and index orphan pages.
Airtight site architecture is an absolute must if you run an eCommerce store with dozens of product pages. That’s because a messy site structure can get out of control fast, and fixing it can be a nightmare if your website has thousands of pages.
An unorganized site structure also makes it extremely difficult to identify and resolve indexing issues, which is a headache that you don’t need.
How can you find out what your site architecture looks like?
Visual Site Mapper is an excellent free technical SEO tool that provides a visual representation of your internal linking structure that’ll help you avoid orphan pages. You can also use our free SEO Audit tool for in-depth insights into technical SEO factors like page load speed, link structure, and more.
Use a uniform URL structure
How you structure your URLs is as crucial as your site structure – and yes, the two are directly related.
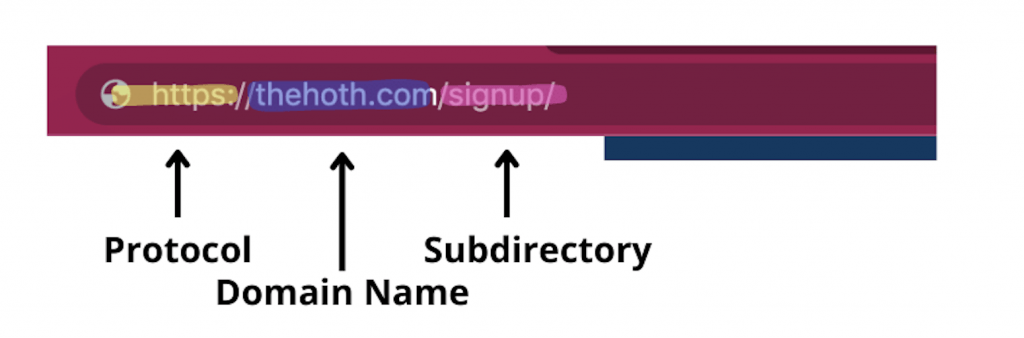
URLs have subfolders (i.e., www.mysite.com/blog) and subdirectories (i.e., blog.mysite.com).
It’s crucial to know the distinction between the two when deciding on the structure for your URLs.
Most importantly, once you decide on a URL structure, it needs to be set in stone. Consistency matters for URLs, and you’ll confuse both bots and online users if you stray from the formula.
Also, try making your URLs short and to the point. There’s no need to muddy the waters with lengthy descriptions of each web page. Other best practices include only using lowercase characters, using dashes to separate words, and including target SEO keywords.
Categorizing your pages is another great idea that’s helpful to bots & users.
Your online users will always know where they are on your website if you categorize your pages logically (i.e., grouping together resources, tools, and blogs in specific categories).
In addition, Google’s crawlers like knowing what role a page plays in the larger context of the website, as evidenced by this quote from Google’s Search Engine Central. So if your pages are categorized, crawlers will be able to garner more context about them, which can help your rankings.
Create & upload an XML sitemap to Google Search Console
Once you’ve got a well-organized site structure in place, you need to create an XML sitemap for it.
What’s that?
A sitemap is a file that serves as a blueprint for your site structure, containing information about all the web pages, pictures, images, and videos on your website.
There are two distinct types of sitemaps, HTML sitemaps and XML sitemaps.
An HTML sitemap is a series of hyperlinks to help users navigate your website. You tend to see them at the very bottom of websites, where there’s an archive of hyperlinks – typically in different categories like Company, Products, and Resources (you can see our HTML sitemap at the bottom of our homepage).
XML sitemaps, on the other hand, help search engines better navigate your website. An XML sitemap will let crawlers know how many pages your website has and exactly where to find them. That means you’ll have a much better chance of getting 100% of your web pages crawled & indexed.
There are plenty of XML sitemap generators online that make creating one very easy.
Once you have one ready, you need to manually upload it to Google Search Console & Bing Webmaster Tools (if your SEO strategy includes Bing).
If you aren’t already set up on GSC, check out our extensive guide on Google Search Console.
Once you log in to GSC, go to Indexing > Sitemaps from the sidebar. From there, all you have to do is copy & paste the URL of your sitemap and hit submit, and Google will have full visibility of your web pages.
It can’t be understated how necessary it is to take this step, as there’s no reason not to upload your sitemaps to ensure proper crawling & indexing takes place.
Leaving a trail of breadcrumbs
The ‘breadcrumbs’ style of navigation is excellent for SEO, as it adds more internal links to your category pages.
Users also love breadcrumbs because they greatly simplify website navigation.
How they work is akin to Hansel and Gretel leaving a trail of breadcrumbs to find their way back home. Whenever a user begins navigating pages on your website, a breadcrumb menu will provide a series of internal links at the top documenting their journey.
Here’s an example of what a breadcrumb menu looks like:
Home > Resources > Learning Hub > Start Learning SEO
As you can see, there’s a trail left behind for every page they visited before ‘Start Learning SEO.’ That way, if a user wants to navigate to a previous page, they can easily do so via the breadcrumbs menu.
Your users aren’t the only ones who benefit from breadcrumbs, though, as bots and web crawlers also use them.
However, for bots to make sense of your breadcrumb menus, you need to add structured data markup language to provide the proper context.
If you aren’t sure how to add structured data to your website, check out our guide on local schema markup.
Robots.txt files & noindex tags
Any time a web robot crawls your website, it has to check your robots.txt file first – AKA the Robot Exclusion Protocol.
What’s that?
It’s a file that gives the power to allow or not allow certain web robots to crawl your website. You can even control whether the bots can access certain web pages or not, which will help you allocate your crawl budget.
There are certain web robots out there that have malicious intent, and they can start posting spam on your website if you aren’t careful. Luckily, you have the ability to ban these bots via a noindex robots meta tag.
Then there are noindex tags that you can use on web pages that you don’t want search engines to crawl & index.
Since you have a crawl budget, you don’t want to waste it on crawling pages that add no value to your SEO profile.
Which types of pages are worth noindex tags?
Here are a few common examples:
- Thank You pages
- Login pages
- Author archives
- Attachment pages
- Admin pages
- Community profile pages
There’s no benefit in generating organic traffic to these types of pages, which is why it’s best to use noindex tags to preserve your crawl budget for more important pages (blogs, videos, podcasts, and infographics).
Canonical tags
Duplicate content is a huge no-no for SEO, as there’s no faster way to confuse web crawlers than by having two near-identical pages.
However, that poses an interesting conundrum for eCommerce website owners, as duplicate content is almost inevitable.
That’s because it’s common to have multiple pages for slightly different versions of the same product. As an example, say you sell cowboy hats online that are available in 10 different colors.
Well, you’ll need to create 10 pages for each hat, and those pages will be duplicates of each other except for one minute detail – the color of the hat.
In these types of situations, you need to use canonical URLs or canon tags.
Here’s the way they work; you set a canon tag on the primary version of the cowboy hat (i.e., the one with default settings). That lets search engines know that it’s the ‘canon’ version of the product that they should crawl & index, all while ignoring the other variations.
That’ll help you avoid duplicate pages while still having unique URLs for each color & size of your cowboy hats.
Optimizing page speed
Next, your site speed is a huge part of technical SEO, so you need to make sure it’s up to par.
Google takes page speed & responsiveness extremely seriously, which is why they developed the Core Web Vitals test that they run on every website. If you don’t pass the test, you won’t show up in the SERPs.
How can you practice for the test?
PageSpeed Insights is a free tool that will help you diagnose loading speed issues on your website.
Beyond that, here are some candid tips for improving your site’s loading times:
- Compressing & optimizing images
- Reduce the number of redirects you have
- Enable browser caching
- Cache your web pages
- Clean up messy Javascript & CSS
- Get rid of unnecessary plugins
Once your page speed is lightning-fast, you’ll pass Google’s test, and your users will enjoy a faster, better experience.
Finding and resolving indexing issues
Lastly, you need to discover if your website has any indexing problems that are holding it back.
What’s the best tool for finding indexing errors?
You guessed it, Google Search Console.
After all, Google’s the #1 search engine online, and GSC will let you know if there are any issues with indexing your web pages.
From the homepage, navigate to the Coverage Report to see if there are any indexing issues that you need to address. Common problems include:
- Soft 404s (301 redirects will fix)
- Redirect errors
- Unauthorized request 401 (usually password-protected pages that you should noindex)
- Blocked due to 4xx issue
Google’s URL Inspection Tool is excellent at fixing these common issues, so don’t hesitate to use it.
Final Thoughts: Technical SEO in 2024
By now, you should have a better understanding of what technical SEO is, why it matters, and why you can’t do without it.
A rock-solid technical SEO strategy is required to achieve top SERP rankings, so you shouldn’t neglect it.
Do you need help with the technical SEO at your company?
Then we’d love to help you at The HOTH, so don’t wait to check out our in-depth managed technical SEO services today.
[ad_2]